About Conference
OMICS International is a renowned organization that organizes highly notable Medical conferences throughout the globe. OMICS International is currently bringing forth “International Conference on Thrombosis and Hemostasis (Thrombosis 2015, Beijing, China)” to be held during November 02-03, 2015 at Beijing, China.
Thrombosis 2015, Beijing, China conveys recent developments and exciting innovations in allied areas of Hematology and it will offer a unique opportunity for investigators from all over the world to meet, network, and perceive new scientific interactions. The theme of the thrombosis conference is “Advances in clinical diagnosis and therapeutic interventions” reflects the emerging progress being made in thrombosis amd hemostasis and other blood related disorders and advances in diagnosis as discoveries in the lab are translated into useful technologies in an increasingly targeted and precise manner. OMICS International planned to organize thrombosis conferences every year.
It has an enhanced and highlighted features of scientific partnerships and alliances with development agencies, Institutes, leading research organizations, non-government organizations, and other entities to promote the development-oriented research across the globe through live streaming, B2B and Scientific Meetings. OMICS International Medical Conferences provides an excellent opportunity for the budding scientist and young researchers through its special initiatives like Young Researcher Forum, Poster Presentation and E-poster at thrombosis conference 2015.
OMICS International Organizes 300+ Scientific Conferences every year across USA, Europe & Asia. Besides 500 Peer reviewed, Open Access Journals, OMICS International has collaborated with more than 1000 Scientific Associations and institutions worldwide to promote information on health care and technologies. These Open Access journals are enjoying the support of over 5 million readers; a team of 30.000 eminent scholars are providing editorial support. To know more about OMICS International conferences please visit conference series.
In China more than 250 Universities/ colleges, 165 pharmaceutical companies, and more than 50 Associations and societies are working on Thrombosis and hemostasis and other blood related disorders. Funding grants by the government of china for research nearly 9 million USD$ to universities and 5 million USD$ to the pharmaceutical and research institutes.
For more information, please visit: Thrombosis Market Analysis
Major Scintiefic Sessions at Thrombosis 2015, Beijing, China
Thrombosis and Current Therapeutic Options
Central venous catheter-related infection and evidence for central venous thrombosis developed in five patients. On the basis of ongoing bacteremia after catheter removal and venography confirmation, catheter-related septic central venous thrombosis was confirmed. These patients were treated successfully with anticoagulation and antibiotics; none required surgical exploration or drainage. CR-SCVT is a complication of modern venous access techniques and is easily confused with sepsis from other anatomic sites. Arterial thrombosis is a blood clot that develops in an artery. It's very dangerous, because it can obstruct the flow of blood to major organs.Arterial thrombosis in eye in this case thrombosis is in the afferent artery of the eye, a passing or permanent closing of the blood vessel affecting the supply area is one of several of the ramifications of the artery. Often, it is only one of the eyes that are affected. The thrombosis is caused by a dislodged blood clot that is lead with the bloodstream and wedges into the eye. Depending on where the clot forms, arterial thrombosis can cause several serious conditions and sometimes can be treated only by thrombosis surgery. Portal vein thrombosis, previously known as Cauchois–Eppinger–Frugoni syndrome, is a form of venous thrombosis affecting the hepatic portal vein, which can lead to portal hypertension and reduction in the blood supply to the liver.
Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinus, a cavity at the base of the brain which drains deoxygenated blood from the brain back to the heart. The cause is usually from a spreading infection in the nose, sinuses, ears, or teeth. Staphylococcus aurous and Streptococcus are often the associated bacteria. Cavernous sinus thrombosis symptoms include: decrease or loss of vision, chemises, exophthalmos, headaches, and paralysis of the cranial nerves which course through the cavernous sinus. This infection is life-threatening and requires immediate treatment, which usually includes antibiotics and sometimes surgical drainage. The clinical presentation of Cavernous sinus thrombosis can be varied. Both acute, fulminant disease and indolent, sub-acute presentations have been reported in the literature. The most common signs of CST are related to anatomical structures affected within the cavernous sinus, notably cranial nerves III-VI, as well as symptoms resulting from impaired venous drainage from the orbit and eye. Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis (SSST) is the most common type of Dural sinus thrombosis and is potentially devastating.This article focuses on the specific features related to the superior sagittal sinus thrombosis, please refer to the dural venous sinus thrombosis article for a general discussion.
Blood Clot and Vein Clot
Blood clots range from deep vein thrombosis to pulmonary embolism. The symptoms of clotting depend on the location of the affected blood vessel and whether the vessel is totally or partially blocked by the clot Blood clots may form in the deep blood vessels, most commonly in the legs and groin, and can block normal blood flow returning from the legs to the heart. Clots in the pulmonary veins lead to pulmonary vein thrombosis or it is also known as pulmonary thrombosis. Clots in vains that form in regions of slow to moderate flow are made of a mixture of red cells, platelets, and fibrin and are known as mixed platelet fibrin thrombi . Clots in the deep veins of the legs or abdomen that partially block the vein may cause subtle symptoms and sometimes may not cause any symptoms until the normal blood flow is significantly disturbed. Venous thrombosis is a blood clot (thrombus) that forms within a vein. Thrombosis is a term for a blood clot occurring inside a blood vessel. A common type of venous thrombosis is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which is a blood clot in the deep veins of the leg. Thromboembolism: Formation in a blood vessel of a clot (thrombus) that breaks loose and is carried by the blood stream to plug another vessel. The clot may plug a vessel in the lungs (pulmonary embolism), brain (stroke), gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, or leg. Thromboembolism is a significant cause of morbidity (disease) and mortality (death), especially in adults. Pulmonary thrombosis treatment may involve anticoagulants (blood thinners), aspirin, or vasodilators (drugs that relax and widen vessels).
Varicose Veins and Cardio Vascular Thrombosis
Varicose veins are veins that have become enlarged and twisted. The term commonly refers to the veins on the leg, although varicose veins can occur elsewhere. Veins have pairs of leaflet valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards. Leg muscles pump the veins to return blood to the heart, against the effects of gravity. When veins become varicose, the leaflets of the valves no longer meet properly, and the valves do not work. This allows blood to flow backwards and they enlarge even more. Varicose veins are most common in the superficial veins of the legs, which are subject to high pressure when standing. Besides being a cosmetic problem, varicose veins can be painful that time varicose vein surgery needed. especially when standing. Severe long-standing varicose veins can lead to leg swelling, venous eczema, skin thickening and ulceration. Coronary thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel of the heart. This blood clot restricts blood flow within the heart. It is associated with narrowing of blood vessels subsequent to clotting. The condition is considered as a type of ischaemic heart disease. Thrombosis in heart can lead to a myocardial infarction. Cardiovascular disease is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. Common CVDs include: ischemic heart disease stroke, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, aortic aneurysms, cardiomyopathy, atrial fibrillation, congenital heart disease, endocarditis, and peripheral artery disease, among others. Acute coronary syndrome is a term used for any condition brought on by sudden, reduced blood flow to the heart.
Thrombosis and Hemostasis beyond Cardiovascular Disease
Congenital heart disease and children with acquired heart disease are patients at risk for clinically significant thrombosis. These include intracardiac, intravascular, and coronary thrombosis; thrombosis of implanted devices and shunts; and thromboembolic stroke. Thrombosis and its management and complications are now increasingly recognized as important factors contributing to their morbidity and mortality. Majority of autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders are linked to an increased risk of venous thrombosis, PE, or VTE. For instance, a Swedish nationwide study found that the risk of PE was increased in the first year after hospitalization for 33 different autoimmune disorders. The close relationship between cancer and thrombosis has been known since the days of Armand Trousseau, who first described the clinical association between idiopathic venous thromboembolism (VTE) and occult malignancy in 1865. Today, we know that cancer is associated with a hypercoagulable state and a four-fold increase in thrombosis risk, with chemotherapy elevating this risk even more. Investigate oral administration of aqueous extracts of Barleria lupulina (AE-BL) for remedying ischemia-driven dysfunctional angiogenesis in mouse models, and define benefits for tissue oxygenation and survival. Pediatrics and Thrombosis incidence of venous thromboembolism, a leading cause of adult morbidity and mortality, is lower in children than in it is in adults, the morbidity associated with it is clinically significant.
Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinus, a cavity at the base of the brain which drains deoxygenated blood from the brain back to the heart. The cause is usually from a spreading infection in the nose, sinuses, ears, or teeth. Staphylococcus aurous and Streptococcus are often the associated bacteria. Cavernous sinus thrombosis symptoms include: decrease or loss of vision, chemises, exophthalmos, headaches, and paralysis of the cranial nerves which course through the cavernous sinus. This infection is life-threatening and requires immediate treatment, which usually includes antibiotics and sometimes surgical drainage. The clinical presentation of CST can be varied. Both acute, fulminant disease and indolent, sub-acute presentations have been reported in the literature. The most common signs of CST are related to anatomical structures affected within the cavernous sinus, notably cranial nerves III-VI, as well as symptoms resulting from impaired venous drainage from the orbit and eye. Superior sagittal thrombosis sinus (SSST) is the most common type of Dural sinus thrombosis and is potentially devastating.This article focuses on the specific features related to the superior sagittal sinus thrombosis, please refer to the dural venous sinus thrombosis article for a general discussion.
Blood Clot and Vein Clot
Blood clots range from deep vein thrombosis to pulmonary embolism. The symptoms of clotting depend on the location of the affected blood vessel and whether the vessel is totally or partially blocked by the clot Blood clots may form in the deep blood vessels, most commonly in the legs and groin, and can block normal blood flow returning from the legs to the heart. Clots in the veins that form in regions of slow to moderate flow are made of a mixture of red cells, platelets, and fibrin and are known as mixed platelet fibrin thrombi. Clots in the deep veins of the legs or abdomen that partially block the vein may cause subtle symptoms and sometimes may not cause any symptoms until the normal blood flow is significantly disturbed. Venous thrombosis is a blood clot (thrombus) that forms within a vein. Thrombosis is a term for a blood clot occurring inside a blood vessel. A common type of venous thrombosis is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which is a blood clot in the deep veins of the leg. Superficial venous thrombosis or superficial thrombosis is inflammation and clotting in a superficial vein.
Infection, Inflammation inThrombosis
Infection and inflammation almost invariably lead to hemostatic abnormalities, ranging from insignificant laboratory changes to gross activation of coagulation that may result in localized thrombotic complications or systemic intravascular fibrin deposition. Proinflammatory cytokines, immune cells, and the endothelium play a central role in the differential effects on the coagulation and fibrinolysis pathways. No studies are available on changes in the polymorph nuclear leukocytes, which can play an important role in the activation of the hemostatic system. Analysis of expression of various cell surface receptors allows characterization of the different monocyte subtypes phenotypically, whereas downstream assessment of inflammatory pathways provides an insight into their activity. Transfusion medicine is the branch of medicine that is concerned with the transfusion of blood and blood components.
Experimental Models and Issues of Thrombosis
Reversal of NOADs in Animal Models Understanding of the potential usefulness and limitations of specific animal models and agents is important because of the imminent risk of thrombosis with such antagonists in high-risk patients. Animal studies of anti-IIa and -Xa drugs are said to widely vary due to differences of animal types, timing, location and extent of vascular injury, and the use of tests such as prothrombin and activated partial thromboplastin time, which are not suitable for monitoring these drugs, or for predicting therapeutic effects of hemostatic agents. An early invasive strategy following thrombolysis for ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction is associated with significant changes in the levels of inflammatory and thrombotic biomarkers, a sub study of the Norwegian study on district treatment of STEMI shows. Sigrun Halverson and team explain that elevations of proinflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, and coagulation markers have been associated with adverse clinical outcomes, whereas elevations of anti-inflammatory biomarkers such as interleukin -10 have been linked to a more favorable prognosis. An evaluation of patients with abnormal bleeding symptoms requires an objective assessment of the bleeding history, a physical examination, a careful drug history and followed by laboratory investigation. Numerical and Platelet function disorders are common amongst patients with abnormal bleeding and may be clinically indistinguishable from other homeostatic disorders. It is probable that because of the complexity of platelets and the difficulty in investigating them, that we under diagnose disorders of platelet function
Platelet Disorders
Platelets are cell fragments that function in the clotting system. Thrombopoietin helps control the number of circulating platelets by stimulating the bone marrow to produce megakaryocytes, which in turn shed platelets from their cytoplasm. Thrombopoietin is produced in the liver at a constant rate and its circulating level is determined by the extent to which circulating platelets are cleared, and possibly by bone marrow megakaryocytes. Platelets circulate for 7 to 10 days. About one third are always transiently sequestered in the spleen. The platelet count is normally 140,000 to 440,000/μL. However, the count can vary slightly according to menstrual cycle phase, gestational thrombocytopenia and increase in response to inflammatory cytokines. Platelets aspects are eventually destroyed by apoptosis, a process independent of the spleen. Antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin, keep blood clots from forming. Many doctors now prescribe aspirin to heart patients for this reason. Thrombocytopenia and thrombopenia refer to a disorder in which there is a relative decrease of thrombocytes, commonly known as platelets, present in the blood.
Hemorrhagic Diathesis and Coagulation Factors
Hemorrhagic diathesis is an unusual susceptibility to bleeding mostly due to hypercoagulability, in turn caused by a coagulopathy. Several types are distinguished, ranging from mild to lethal. Also, bleeding disorders can be caused by thinning of the skin or impaired wound healing. Coagulation involves both a cellular and a protein component. The system in humans has been the most extensively researched and is the best understood. Coagulation begins almost instantly after an injury to the blood vessel has damaged the endothelium lining the vessel. Exposure of blood to the space under the endothelium initiates two processes: changes in platelets, and the exposure of subendothilial tissue factor to plasma FactorVII, which ultimatelleadsto fibrin formation. Coagulation factors are Calcium, phospholipid, Vitamin K. Blood clotting proteins Fibrinogen A specialized protein or clotting factor found in blood. When a blood vessel is injured, thrombin, another clotting factor, is activated and changes fibrinogen to fibrin. Atrial fibrillation is the most common sustained arrhythmia,1 affecting approximately 2.3 million people in the United States. Rare clotting factor deficiencies are a group of inherited bleeding disorders caused by a problem with one or several clotting factors. Clotting factors are proteins in the blood that control bleeding. Many different clotting factors work together in a series of chemical reactions to stop bleeding. This is called the clotting process.
Importance & Scope
Summary
Thrombosis 2015, Beijing, China welcomes attendees, presenters, and exhibitors from all over the world to Manchester, UK. We are delighted to invite you all to attend and register for the “ International Conference on Thrombosis and Hemostasis (Thrombosis-2015)” which is going to be held during November 02-03, 2015 in Beijing, China.
The organizing committee is gearing up for an exciting and informative conference program including plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at the Thrombosis 2015 Beijing, China, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world. All members of the Thrombosis 2015, Beijing, China organizing committee look forward to meeting you in Beijing, China.
For more details please visit- http://thrombosis-hemostasis.conferenceseries.com/
Importance & Scope
The Important of Thrombosis-2015 is to update, clinically relevant audience regarding the evidence supporting current Advances in diagnosis of Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Researchers and scientists whole over the world can exchange ideas and views. Students from different universities gather together and improve their knowledge. Pharmaceutical companies can exhibit their new products and research and development methods.
Thrombosis 2015, Beijing, China is an international platform for presenting research about, exchanging ideas about it and thus, contributes to the dissemination of knowledge in research techniques in diagnosis and prevention of blood disorders for the benefit of both the young researchers, scientists, Pharmaceutical companies and Academia. Thrombosis 2015, Beijing, China is where the future of exhibit new Diagnostics methods and Instruments used for treatment and diagnosis and novel drugs. This event brings together senior brand marketers and agency executives to explore marketing and advertising opportunities on Pharmaceutical companies.
Why Beijing?
Beijing formerly Romanized as Peking is the capital of the People’s Republic of China and one of the most popular cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The metropolis, located in northern China is governed as a direct-controlled municipality under the national government, with 14 urban and suburban districts and two rural counties. Beijing Municipality is surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin Municipality to the southeast.
Beijing is China’s second largest city by urban population after Shanghai and is the country’s political, cultural, and educational center and home to the headquarters for most of China’s largest state-owned companies. Beijing is a major transportation hub in the national highway, expressway, railway and high-speed rail network. Beijing’s Capital International Airport is the second busiest in the world by passenger traffic. In China more than 250 Universities/ colleges, 165 pharmaceutical companies, and more than 50 Associations and societies are working on Thrombosis and hemostasis and other blood related disorders. Funding grants by the government of china for research nearly 9 million USD$ to universities and 5 million USD$ to the pharmaceutical and research institutes.
Conference Highlights
-
Thrombosis and Current Therapeutic Options
-
Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
-
Blood Clot and Vein Clot
-
Varicose Veins & Cardio Vascular Thrombosis
-
Thrombosis and Hemostasis beyond Cardiovascular Diseases
-
Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders in Thrombosis
-
Infection, Inflammation and Thrombosis
-
Experimental Models and Issues of Thrombosis
-
Hemorrhagic Diathesis and Coagulation Factors
-
Platelet Disorders
-
Thrombosis Diagnosis and Advanced Therapeutics
-
New Issues and Developments in Thrombosis and Hemostasis
-
Transfusion Medicine and Hematology Research
-
Venous Thromboembolism Diagnosis and Treatment
Why to attend?
Conferences share a lot of knowledge to Universities, companies. It benefits to medical students and researchers as well as professors and lab technicians. Conferences also benefits and share knowledge between scientist, doctors and delegates. One company networks with the other company and they share knowledge to each other about their product at the conference. The companies come to attend conferences and show their exhibit in front of eminent members and delegates present at the Conference.
A Unique Opportunity for Researchers and Exhibitors at this International event:
http://thrombosis-hemostasis.conferenceseries.com/abstract-submission.php
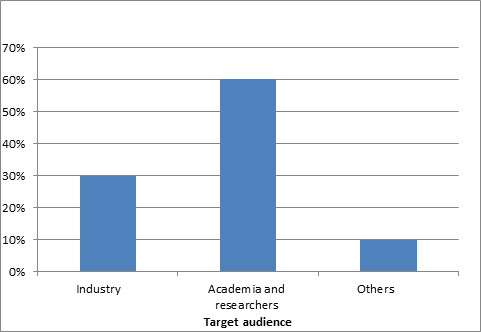
Target Audience
Scientists, Researchers, Young Scientists, Professors, Deans, Physicians, Students, Academia, Directors/Managers, Departmental Managers, Vice Presidents/ Directors & Brand Manufacturers/ Marketers of Consumer Products. Retailers, Marketing, Advertising and Promotion Agency Executives.
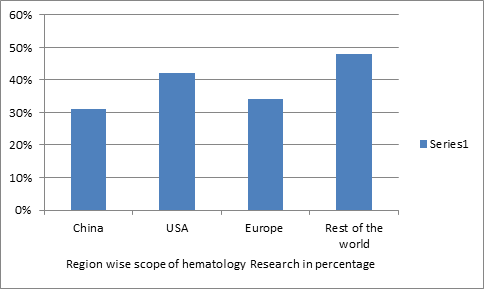
Region wise scope of thrombosis and hematology resarch
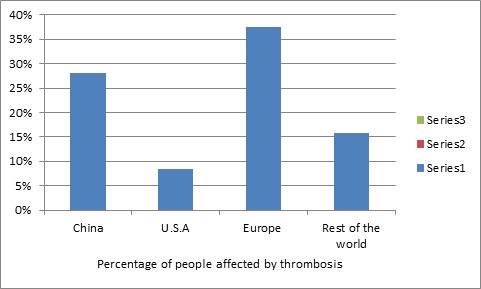
Percentage of people affected by thrombosis
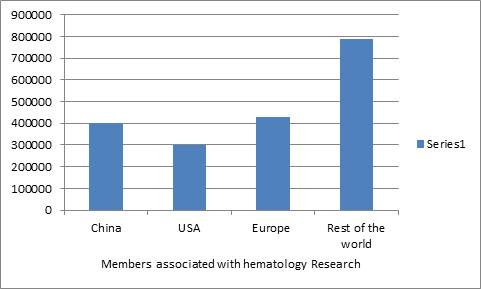
Members associated with hematology Research
Hospitals related to thrombosis & hemostasis
China
Institute of Hematology
Beijing sihijitan hospital
Peking Union Medical College Hospital
West China Hospital
Ruijin Hospital
Xijing Hospital
Zhongshan Hospital
Huashan Hospital
Peking University First Hospital
Tongji Hospital
USA
Children’s hospital LA
Ucsf benioff children's hospital Oakland
Jones hopkins pathology
St.james hospital
St. Michael's hospital
Newyork-presbyterian hospital
Mayo clinic hospital, phoenix
Scottsdale healthcare shea medical center
Alta bates summit medical center alta bates campus
California pacific medical center california campus
Hoag memorial hospital Presbyterian
Europe
Charing cross hospital
Hammersmith hospital
Queen charlotte’s & Chelsea hospital
St. mary’s hospital
Skane university hospital, malmo
St. James hospital, Dublin
St. Thomas hospital
Tri-square general hospital, Taipai
University hospital
Rest of the World
Chidren’s hospital
Levine Children’s Hospital
Oxford university hospitals
Cleveland Clinic
Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston
Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore
Mayo Clinic in Rochester

Universities related to thrombosis & hemostasis
China
Peking University
Xiamen university
Weifang Medical University
Huazhong University of Science and Technology
University of Science and Technology Beijing
Nanjing University of Science and Technology
East China University of Science and Technology
Peking University
Shanghai University
Fudan University
Zhejiang University
Sun Yet-Sen University
Sichuan University
Central South University
Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine
Capital Medical University
China Medical University
USA
George Mason University
Missouri University of Science and Technology
Northeastern University
Polytechnic Institute of New York University
Rochester Institute of Technology
San Francisco State University
Southern Methodist University
State University of New York Binghampton
State University of New York Plattsburgh
University of South Florida
Washington State University
University of Maryland Medical Center
Europe
Maastricht University
International Medical School
Humanitas University Medical School
Sapienza University Di Roma
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Medical university of cdanska
San raffaele university
Medical university of lodz
The university of buckingum
School of medicine in Katowice
Rest of the World
Harvard University
University of Cambridge
University of Oxford
Stanford University
University of California, Berkeley (UCB)
Yale University
California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA)
Imperial College London
University of Toronto
Johns Hopkins University
Columbia University
University of Pennsylvania
McGill University
Princeton University
University of Chicago
Arizona State University
University of Michigan
University of British Columbia
Duke University
The University of Melbourne

Associations related to thrombosis & hemostasis
China
The Hematology Society of Taiwan
APHCON Executive Committee
Chinese Society of Hematology
Chinese medical doctor association
Chinese Society of Medical History
Chinese Society of Medicine
Chinese Society of Surgery
Chinese Society of Popular Medical Sciences
Chinese Society of Oncology
Chinese Society of Medical Education
Chinese Society of Radiation Oncology
Chinese Society of Emergency Medicine
Chinese Society of Medical Information
China Healthcare Association
China TCM & Western Medicine Integration Association
China Medical Laboratory Association
China Children's Health Association
China Hematology Association
China Blood Transfusion Association
USA
American society of hematology
American society of pediatric hematology/ oncology
American medical association
American medical news
California medical association
Society of hospital medicine
America's blood centers
American public health association
The North American society on thrombosis and hemostasis
Hemostasis and thrombosis research society
North American thrombosis forum
British society for Haemostasis & thrombosis
Europe
European society of cardiology
International society of thrombosis and Haemostasis
International Board for Medical Research and Studies
European Society for Medical Oncology
Association of the Scientific Medical Societies in Germany (AWMF)
German Agency for Quality in Medicine
German Medical Association
German Network for Evidence Based Medicine
Irish Medical Organization
British Medical Association
Royal Medical Society
Rest of the world
World medical association
Hemostasis and thrombosis research society
The Japanese society on thrombosis and hemostasis
Australian medical association
Canadian medical association
Brazilian medical association
Gynecologic oncology group
Australasian college for emergency medicine
Australian medical association
Australian and new zealand college of anaesthetists
Doctors reform society of Australia
National prescribing service
Royal australasian college of surgeons
College of community physicians of sri lanka
Society of hospital medicine
Urgent care association of America
Association of american physicians and surgeons
National association of emergency medical technicians
Royal college of surgeons of England
Royal college of surgeons of edinburgh

Companies related to thrombosis & hemostasis
China
Midray
Micro port
LEPU medical
Fosun pharma
Realmed ltd.
Sysmex
STAC
ERMA
Nihon kohden
Abx/beckman coulter
Malaya healthcare solutions
OEM corporations
ERBA diagnostic
Shenzhen prokan
Aspen pharma
USA
Boehringer ingelheim pharmaceuticals
Machaon diagnostics, thrombosis & hemostasis lab
Sanofi Aventis
Isis pharmaceuticals
Med gadaget
Biobase
Hi tech surgico
ICUIBO
Astellas pharma
Baxter international
Actavis pharmaceuticals
Allergen
Eisai.Co
Pfizer
Europe
Abiogen Pharma S.p.A.
Alfa Wassermann S.p.A.
Almirall, S.A.
Menarini Industrie Farmaceutiche Riunite Srl
Antibiotics SA
AstraZeneca
Bayer HealthCare AG
Betapharm Arzneimittel GmbH
Bilim Pharmaceuticals
Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH.
Combino Pharm, S.L.
Desitin Arzneimittel GmbH
Deva Holding AS
Dompé Farmaceutici S.p.A.
Egis Pharmaceuticals PLC
Elpen Pharmaceutical Co. Inc.
Faes Farma, S.A.
Ferring International Center S.A.
Galderma Pharma SA
Gedeon Richter Plc
Genepharm Group
Giuliani S.p.A. Laboratórios Basi Industria Farmacêutica, S.A.
Laboratorios Cinfa S.A.
Laboratorios Dr. Esteve, S.A.
Laboratorios Farmacéuticos Rovi, S.A.
Laboratori Guidotti SpA
Laboratorios Salvat S.A.
Rest of the world
Merck
Sanofi
GlaxoSmithKline
Gilead Sciences
Novo Nordisk
Amgen
Astellas
Daiichi Sankyo
Otsuka Holdings
Gilead Sciences
Merck KGaA
CSL
Allergan
Shire
Dainippon Sumitomo
Leo Pharma
Novartis International AG
Novo Nordisk A/S
Nycomed International Management GmbH
Orion Corporation
Pierre Fabre
Pliva d.d.
Polifarma S.p.A.
Polpharma S.A.
Ratiopharm GmbH
Recordati S.p.A.
Remedica Ltd.
Riemser Arzneimittel AG
Rottapharm SpA
Sandoz International GmbH
Sanitas AB
Sanochemia Pharmazeutika AG
Servier International

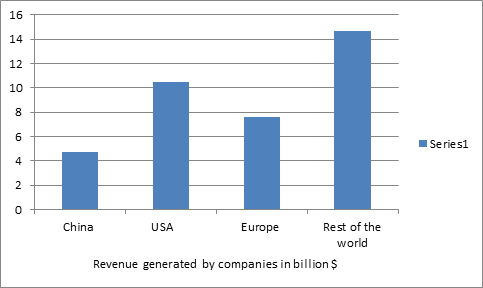
Glance at Market of thrombosis and Hematology
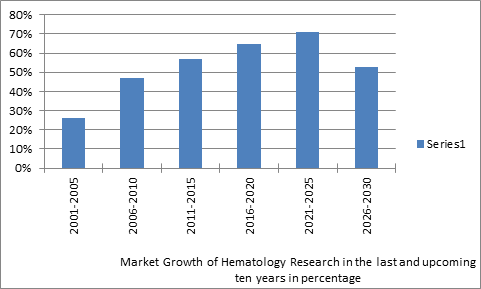
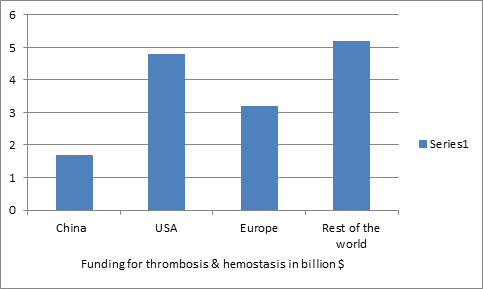
According to market study, market value of thrombosis and hematology at present is $20.45 billion. About 30-40% people in Europe and average about 15% of world’s population is affected by thrombosis. A major part of research is going on at the top Universities across the globe, on Thrombosis and Hematology and the grants allotted for this research field is around $15.34 billion. Many companies are associated with the Thrombosis and blood testing equipment along with various diagnostic instruments, solutions and reagents related to diagnostics, Thrombosis and hematologic drugs and other therapeutics, the revenue generated is around $37.14billion on average by these companies across the globe. Besides this various societies and research labs are also associated in this research field. More than 30% research work on Hematology is going on in China as around 120 Universities in China are working in this field, along with 80 Societies and associations, besides that there are almost 30 companies which deals with diagnostic and testing equipment along with many international and domestic pharmaceutical companies are in China. Market value of Hematology at present in China 2.1 billion at present, university grants allotted by government is about $1.8 billion and average revenue generated by the industries in China is $4.2 billion. The global thrombosis and hematology market is divided into hematology and thrombosis products, Thrombosis and Hematolgy conference & services. The thrombosis and hematology products and reagents segment holds the largest share of the market in 2015. Thrombosis and hematology conference-2015. it is also expected to grow at the highest growth rate by next five years, owing to the increasing development of new hematology reagents. In addition, to Thrombosis and hematology conference-2015 is based on the end-users, the global hematology market has been segmented into commercial organizations, stand-alone hospitals, research institutes, and clinical testing labs. The clinical testing labs hold the largest share of the Hematology market 2015.
Market Growth of Hematology Research in the last and upcoming ten years